From Cultured Meat to 3D Food Printing, these 3 Innovations Are Changing the World of Food Production
The food-tech space is booming with new projects and developments to solve some of the biggest concerns of modern food production. It is clear that our current means of food production are no longer sustainable and that our efforts to produce more food are taking an environmental toll on the planet. However, technology is moving fast, and many organizations are working hard to find better solutions to our food production limitations. These three food tech innovations might be the future of sustainable eating.
At UpMeals, we love seeing how new innovations disturb the food production system, so we decided to take a deeper look into some of the wildest food innovations that are changing the way we make food. Some of these might seem like they’ve been pulled out of a sci-fi movie, but they may be on the road to becoming some of the biggest trends and most innovative solutions to many challenges in the food production space. Check them out!
Making protein out of thin air
We know what you’re thinking, but creating protein out of thin air might be a possible future for protein production. This process is currently being researched by Solar Foods Ltd. a Finish company dedicated to making high-quality protein from air, water, and electricity.
The Solar Food efforts were born as a response to the climate crisis and the large role that agriculture plays in climate change. The company is dedicated to disconnecting food production from agriculture altogether, reducing the carbon footprint and land use involved in the production of meat products. The creators of Solar Foods and their new technology Solein claim that this process is 100 times more climate-friendly than meat.
As if this all didn’t seem wildly futuristic, check this out: Solar Foods is working with the European Space Agency to bring this technology to astronauts in orbit.
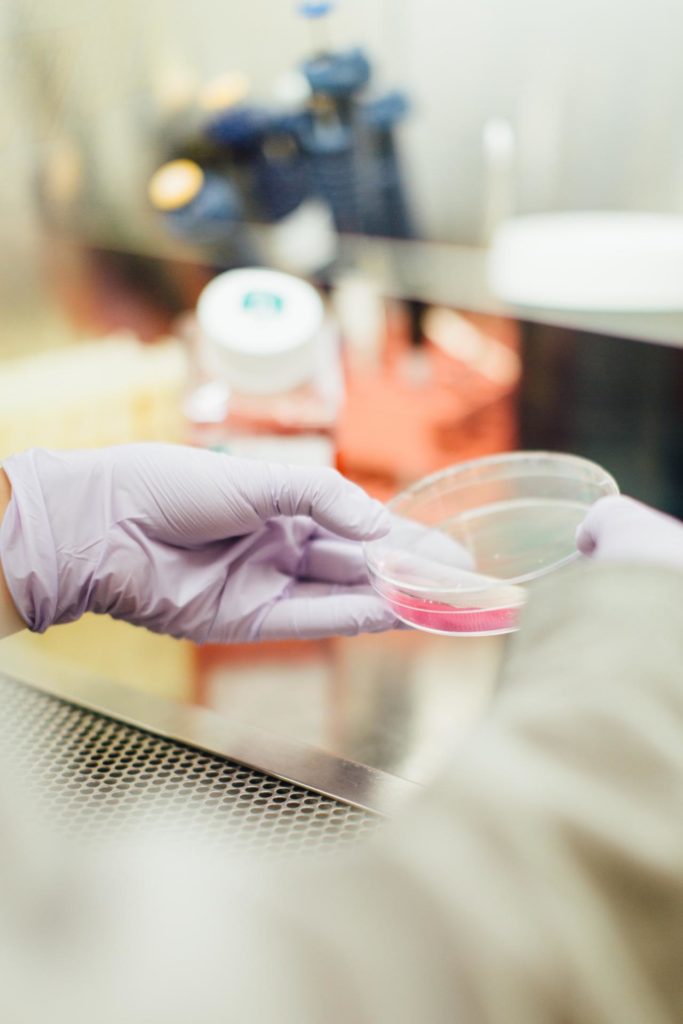

How does Solein work?
The process works in a similar way as beer brewing. It starts with a microbe grown in a fermentation tank. This microbe thrives on certain nutrients, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen bubbles.
The company creates nitrogen by applying electricity to water and feed it to the fermenting microbe along with specific vitamins and nutrients.
The end product of this unique process is a powder that has a protein content of up to 65%. The rest of the product contains carbohydrates and fats, making it a balanced, high protein product.
The powder can be added to products like bread and pasta to increase their protein content. It can also potentially be used to feet culture meat processes.
Is it cost-effective and accessible?
The company states that their production costs could compete with those of other meat and plant-based protein sources at around 5-6 dollars for every kilogram of protein.
The company’s goal is to place Solein products in the market by 2021 after its funding and escalation efforts.
Keep an eye out for these innovative meals that are getting ready to hit the market.
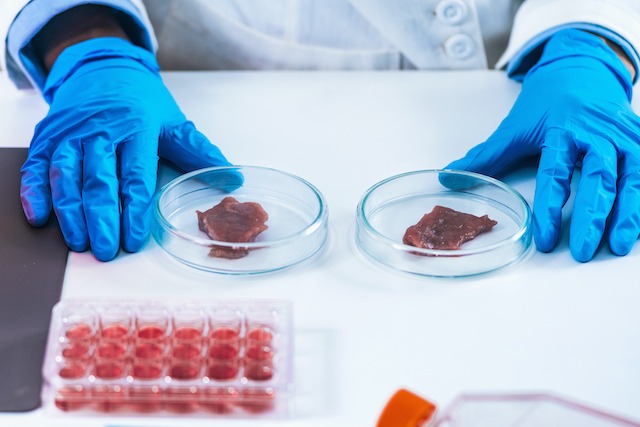
Cultured Meat
Would you eat meat that’s been grown in a lab? Cultured meat might be the future of sustainable meat production, and that future might be closer than you might imagine. In fact, many restaurants around the world are already serving lab-grown meat on their menus.
Dozens of tech companies are working on mastering the art of lab-cultured meat in order to produce meat products comparable in nutrition, texture, and taste to traditional farm-raised meat, but with minimal carbon footprint and no slaughter involved. Some estimates suggest that cultured beef could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 95%!
In 2020 Good Meat, an American company passed a series of safety regulations from the Singapore Food Agency that could open the door to have their cultured chicken products available in restaurants and on the market.
How is cultured meat made?
Cultured meat starts with harvesting muscle cells from livestock, a process that is harmless and minimally invasive to the animal. In controlled laboratory settings, the cells are fed and nurtured so that they multiply and the tissue grows, much like it would on a living body.
Because these cultures are made directly from actual cells from real live animals, the biological components of cultured meat are virtually identical to those of meat you would traditionally get from an animal. This means that everything from nutrient profile to taste and texture is basically the same. This could be the best alternative for meat eaters who are looking for more sustainable sources.
Is it cost-effective and accessible?
The cost of cultured meat has dropped significantly since the first innovation efforts back in 2013. The cost of production back then sat over $300,000 making it a completely inaccessible food source, but the field has gained a lot of momentum, and as production grows and becomes streamlined the cost has significantly dropped and is estimated to reach a price of around $10 per serving in 2021. Still pricy, but way better than 300k right?
A few restaurants already have cultured meat products available on their menus. The Chicken is an Israel based restaurant serving cultured meat products. Their products are created by SuperMeat another big name in the clean meat industry.
3D Printed Foods
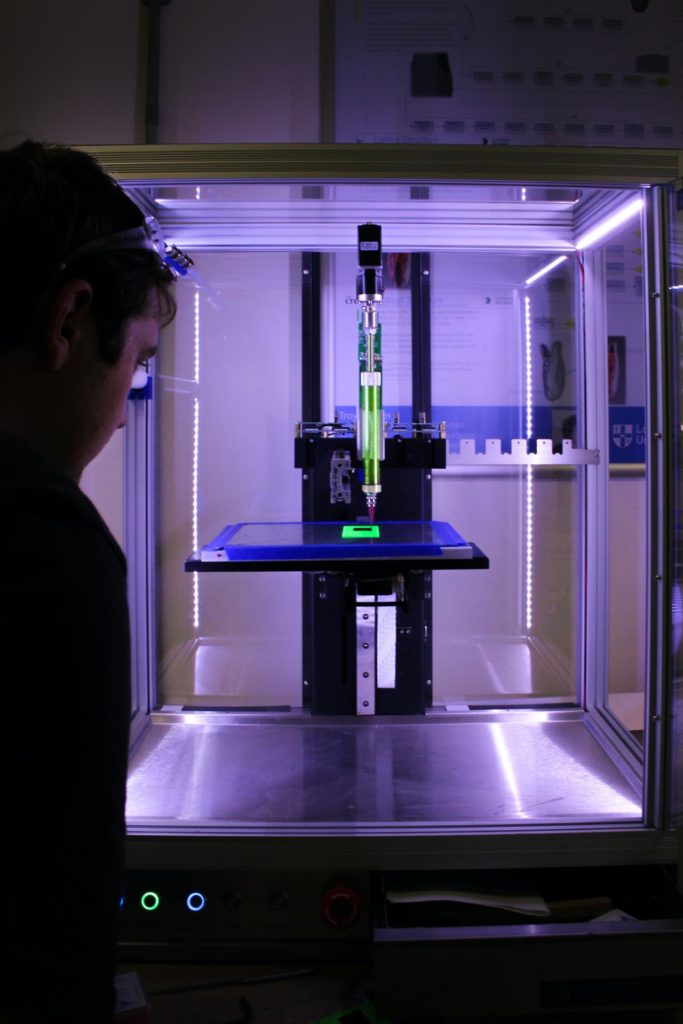
3D printers might become the next big thing in terms of kitchen trends. Imagine creating intricate, customized meals at the touch of a button! This may sound like something that could only happen in a fun dream, but 3D printing is actually already being used to produce different kinds of food.
Many chefs and food designers across the world are using 3D printing and molding technologies to create unique food products that are sure to impress, but the world of 3D food printing is moving even further than just making food in funky shapes. 3D food printing has the potential to bridge the gap between small production facilities and large corporations by providing cost-effective ways to produce large quantities of perfectly crafted products.
This technology can also be used to create completely customized products where dietary, taste, and texture preferences can be used as data input to create a product that meets the needs of the user.
How does 3D food printing work?
3D printers work by depositing the building material through a nozzle that is guided by digital information from a design file. The material is placed one layer at a time slowly building a three-dimensional shape.
In the case of food printing, the “building material” has to be extruded food that meets a certain consistency requirement in order for the final product to hold its shape. The extruded building material can come from a variety of foods and it is a process that is already common in the food industry in the production of pasta, sausages, breakfast cereals, and many more.
Are 3D printers accessible?
Natural Machines created the first printer to produce sweet and savory foods, and their household-friendly printer, Foodini, is now on the market for general users. Devices like these can help create meals with the touch of a button, but needless to say, having one of these in your kitchen is a luxury that many can’t afford, and at least for now, it is a technology that is not part of the mainstream household cooking scene.
TNO is another organization making strides in the 3D printing world by merging technology and healthy living. They have ongoing efforts to make healthy food as well as pharmaceutical products available through 3D printing.
Learn about UpMeals’ AI-driven solution!